- home
-
Products
- Products
- Metrici LPR
- Metrici LPR Parking Module
- Metrici LPR Toll Station Module
- Metrici LPR Weighing Module
- Metrici PPD
- Metrici Area Counter
- Metrici Line Counter
- Metrici Thermal Analyzer
- Metrici Custom Applications
- Metrici Car Kit
- Metrici Server Systems
- Metrici Observer Radar
- Metrici LED Display
- Metrici MultiController
- Metrici LAN Controller
- Benefits
- case studies
- Resources
- news
- videos
- Contact
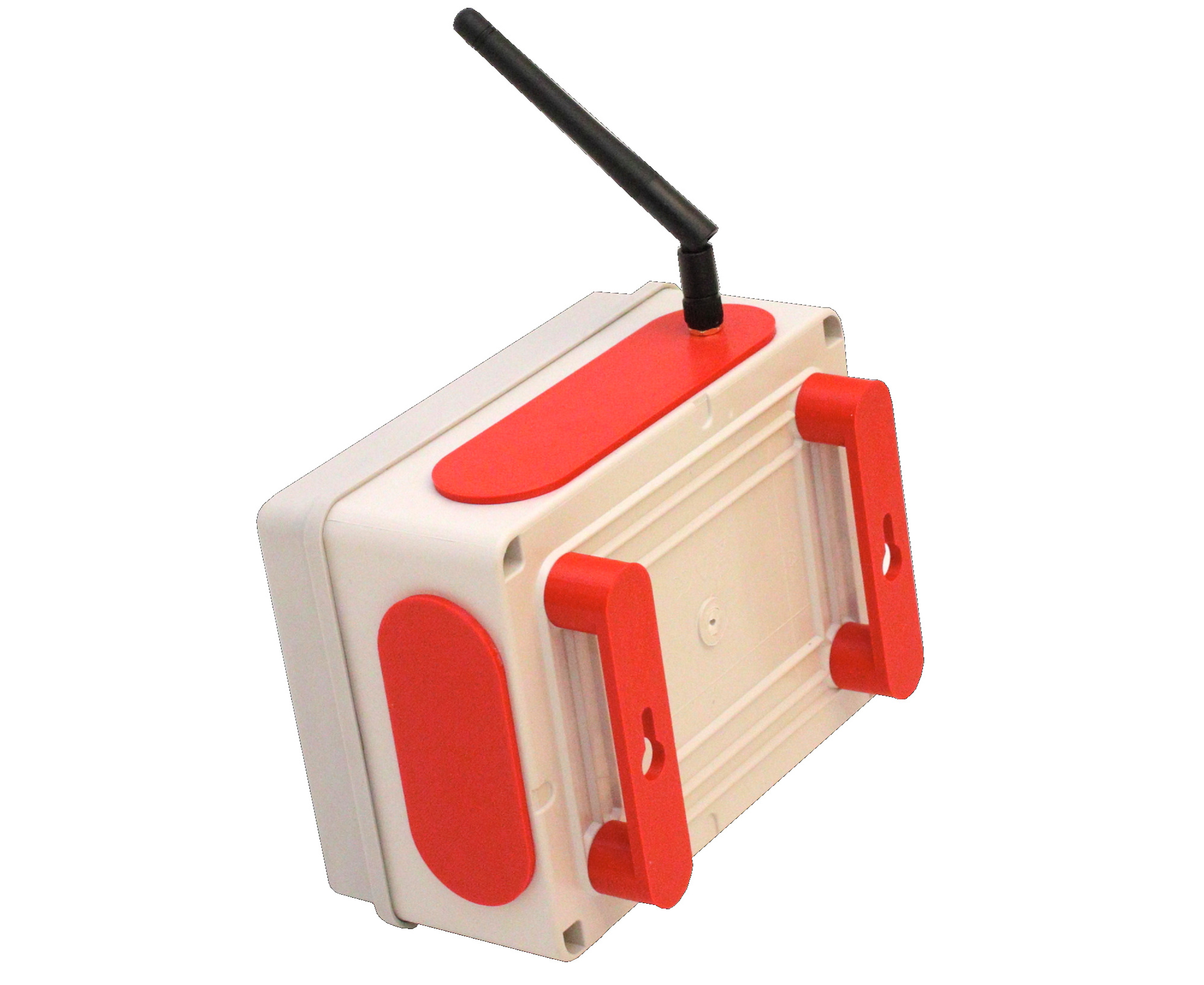
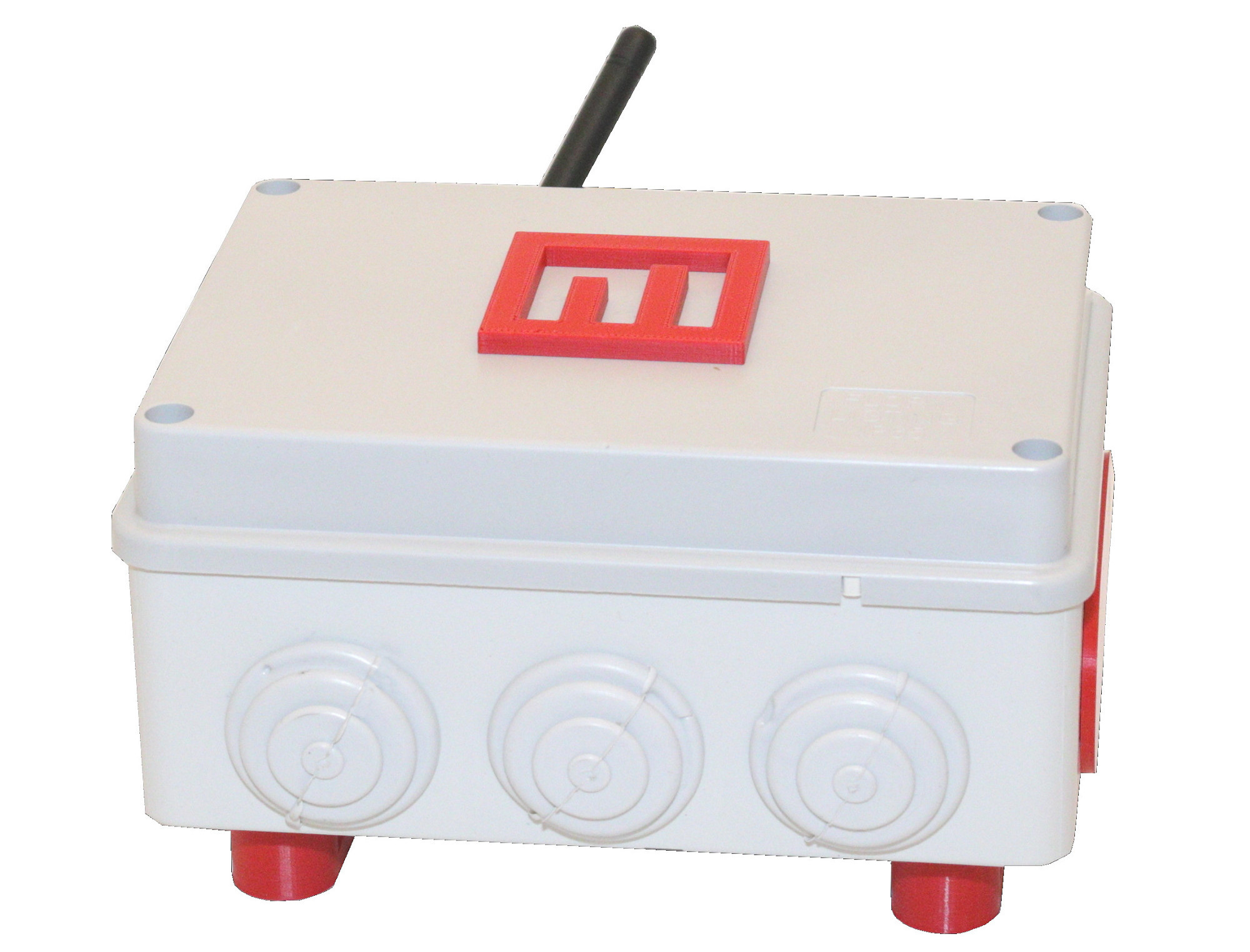
New hardware: Metrici MultiController with Wiegand Protocol
Metrici, the renown Romanian AI specialist in video analytics improves its hardware offer with a new hardware product. The company launches Metrici MultiController which also has the Wiegand Protocol implemented (MMCW).
This LAN Controller is an in house developped product with Wiegand Protocol immplemented as a plus and is a multi-purpose tool in different security, traffic management, access contol scenarios.
The organizations requiring large-scale access control installations, whether in terms of advanced functionality, number of doors/barriers/levels or number of credentials, have a new option . Metrici MultiController with Wiegand Protocol has the abbility to manage a large number of credentials and users.
It has a powerful processor, optimized for the processing of large user credentials and communication with both Metrici database and interface as well as a Wiegand Central Command Station.
Benefits of MultiController include - easy integration, use of existing id badges for a single badge solution, individual settings for each employee, manage from any computer on the network, save energy, money and time.
As the name suggests, the device is multiporpose: it has two digital inputs and two digital ouputs, in addition to the Wiegand Protocol implented on a powerfull processor and it was created to be used in different scenarios.
On one hand it can be used for its Wiegand protocol and linked to access control scenarios, in combination with all Wiegand central stations hardware and and wired connection. On the other hand it can be used as a classical controller with the help of its digitial outputs and inputs and its connectivity.
Also Metrici MultiController has WiFi and Ehernet connection and can be linked to Metrici database and Interface besides to a Wiegand Central, as explained further.
In a first scenario, Metrici MultiController with Wiegand Protocol can be used in connection to two inductive loops or sensors, for example and to trigger Metrici engine to make a detection. In this scenarios, it can also command up to two barriers, two traffic lights or other external hardware via its two digital outputs.
As such, when communicating with Metrici Database and interface, it receives commands to take an action or not for specific license plates when detected.
For example, it may receive a command to make a traffic light red if a car doesn’t have access rights for a parking lot or a street traffic light to change color when more than X cars are waiting in queue .
For a second scenario, MMCW is used for its Wiegand cappabilities. When a license plate is detected, the Metrici Engine does a Check Action to the controller. This, in its turn asks for a wiegand ID to Metrici Database.
If that particular license plate has a Wiegand ID in Metrici database, the Controller receives it and will pass it to Access Control Central Command which makes the call to take an action or not. This action can be opening a barrier, a door, act an external hardware or any other command.
If that particular license plate has no Wiegand ID or the ID has no rights in an area, no action will be completed .
The device can be used as such by companies as a timesheet add-on for the employees.
As many companies are already using Wiegand based cards for employees access, the MultiController with Wiegand Protocol comes as a bonus for securing even more the location and offers a better and wider view of the movement in and out of the location. A single Wiegand interface can be used for the entire location or this one along with the Metrici Interface.
The wiegand IDs used in Metrici can be imported as list or copied one by one from a Wiegand Access Control Central Command . It can also be generated by Metrici, becoming a virtual card assigned to a particular number plate.
What is a Wiegand Device?
Wiegand refers to the technology used in card readers and sensors. This system is a wired communication interface that operates between a reader and a controller. Usually, Wiegand technology is found in cards, fingerprint readers, or any other data-capturing devices. It is commonly used in access control applications.
In a normal situation, a Wiegand reader, or sensor, is used to pick up the information on a Wiegand device. This pieces of information may include
- Credit card numbers
- Bank account numbers
- Employee identification information
- Criminal records
- Medical histories
The good fact is that this information is incredibly difficult to counterfeit or duplicate.
Metrici MultiController communicates in 26 bit Wiegand protocol. 26 bit is the encoding used by the readers and proximity credentials. This protocol in is the industry-standard format of open encoding when it comes to access control systems.
The data encoded using this kind of format offers a huge amount of possible facility codes and unique card numbers. This helps to keep the data more secure in the Wiegand system.
Where to be found a Wiegand Device?
- Access badge
- Office buildings
- State Institutions
- Access control
- Keycard
- Common Access Card
- Credential
- Identity document
- Magnetic stripe card
- Photo identification
- Security (physical, engineering)
- Proximity card
- Security
- Smart card
About Wiegand
John R. Wiegand moved from Germany to the United States in the 1930’s, in order to study piano and choral conducting, but later became an engineer.
Wiegand wire, patented by Wiegand in 1974, is composed of a magnetic iron-alloy which surrounds a softer inner core.
When passed through a magnetized field, the two layers magnetize and switch polarity that creates voltage pulse and these voltage changes are easily detectable.
Late 70’s, Wiegand and his business partner, Milton Velinsky, developed a card using Wiegand wires for access control purposes.
Wiegand format is defined as series of binary data transmitted over the two output wires. The industry standard for the first decade and still the most used today was a 26-bit format. The Wiegand interface remains the standard convention for the transmission of data for any device (card, biometric, or PIN reader) to an access control panel.